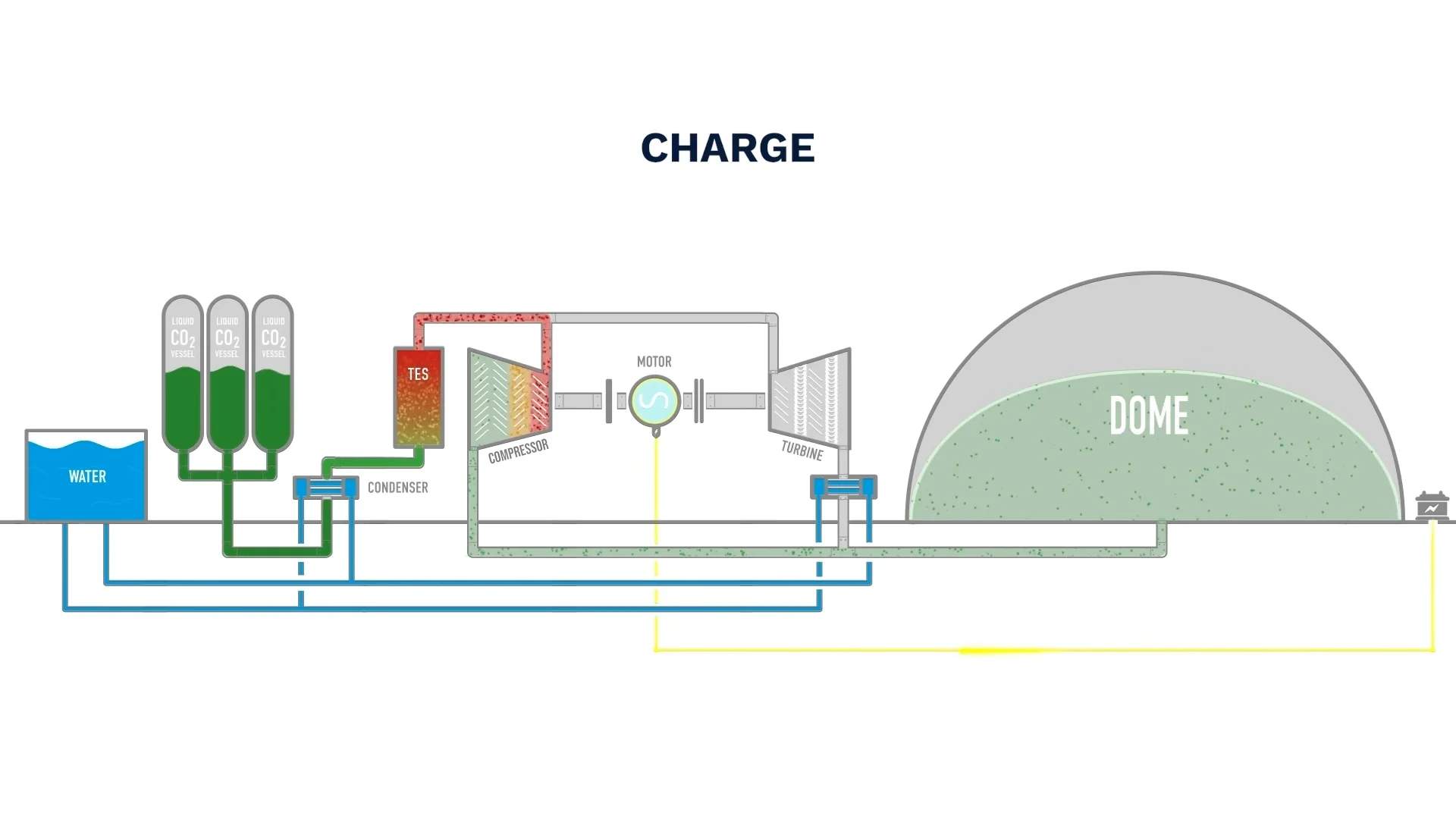
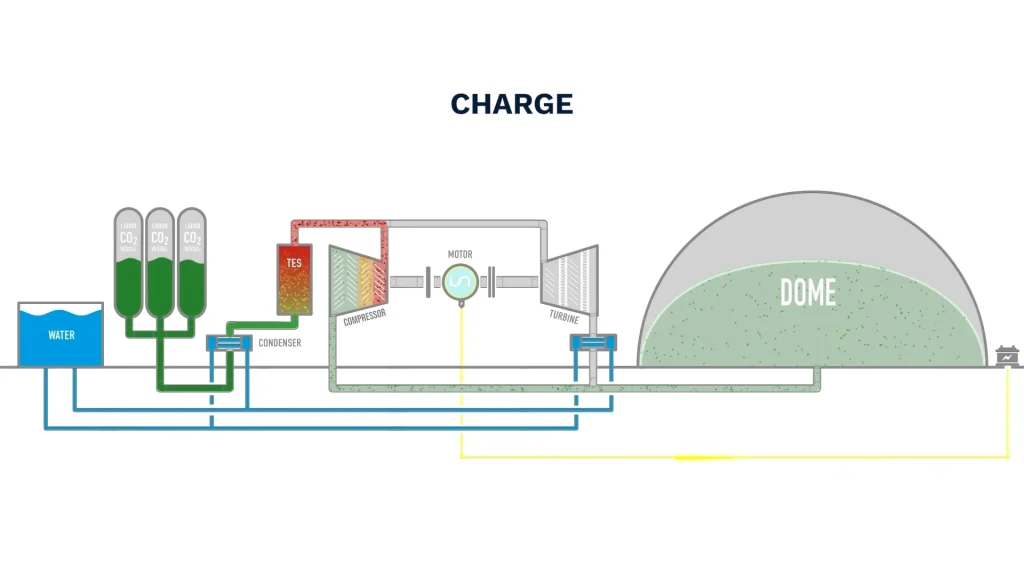
二氧化碳充电技术,正式名称为超临界二氧化碳(S-CO2)储能和发电技术。它代表了一种创新的能源存储和转换方法。这种方法利用了二氧化碳在超临界状态下的独特性质——高于31.1°C和7.38 MPa。在这种状态下,二氧化碳表现出气体和液体的特性,能够实现高效的能量转换。这种电能和热能的双重储存和释放使S-CO2技术成为能源领域的突破性解决方案。
二氧化碳充电技术是如何工作的?
储能阶段(充电)
- 压缩储存:在非高峰时段或可再生能源充足时,二氧化碳气体在环境温度下储存。此外,压力被压缩到超临界状态。即压力>7.39 MPa,温度≥31.1°C。这种压缩产生的热量储存在熔融盐等材料中。
- 冷却和储存:超临界二氧化碳随后被冷却成液态或高压气体,并储存在隔热储罐中。这实现了压力和热能的双重存储。
能量释放阶段(放电)
- 加热和膨胀:高压液态二氧化碳被释放、加热并吸收储存的热能,转化为高温高压气体。
- 涡轮机发电:这种高压气体驱动涡轮机发电。膨胀后的气体被冷却并恢复到初始状态,准备进行另一个循环。
核心系统组件
- 闭环系统:包括压缩机、涡轮机、热交换器(再生器、预热器)和储热罐(高温和低温)。闭环设计确保了最小的二氧化碳损失,最大限度地提高了效率。
- 储热系统:利用熔融盐和固体陶瓷等材料,该系统储存压缩过程中产生的废热。通过这种方式,它大大提高了能源利用效率。
核心优势和技术特点
超高能量转换效率
传统的汽轮机系统以约35%至40%的效率运行。相比之下,当与700°C以上的高温热源结合使用时,S-CO2布雷顿循环的效率可达45%至55%。由于超临界CO2的低粘度、高导热性和高密度,这比传统系统提高了15%至20%,从而降低了管道阻力和设备尺寸。桑迪亚国家实验室的测试表明,在650°C的热源条件下,S-CO2循环的效率比蒸汽循环高12%,在相同的功率输出下,热输入减少20%。
环保和低碳潜力
- 零排放操作:闭环系统确保二氧化碳被回收,没有废物排放。使用从工业过程中捕获的二氧化碳,例如从燃煤发电厂捕获的二氧化碳。这进一步提高了碳利用率,有助于实现碳中和目标。
- 低环境影响:与需要大量水资源的抽水蓄能或具有污染风险的锂电池不同,S-CO2技术占用的土地少得多(蒸汽系统大小的十分之一到五分之一),并使用无毒、不易燃的二氧化碳作为工作介质,提高了安全性。
高能量密度和紧凑设计
超临界CO2的能量密度(约0.5至1.0千瓦时/升)是传统压缩空气储能(0.1千瓦时/L)的5至10倍。这使得设备尺寸减少了60%至70%。例如,额定功率为100 MWh的储能系统需要约500平方米,而同等锂电池系统需要超过2000平方米。
多功能集成能力
S-CO2技术可以与多种热源连接,包括光伏和太阳能热系统、高温气冷反应堆、钢铁和水泥厂的工业废热(300-700°C),甚至可以改造燃煤电厂以实现清洁高效的运行。
快速响应时间
该系统可以在10到15分钟内从冷启动过渡到完全发电。它大大超过了燃煤电厂,燃煤电厂通常需要30多分钟。这种快速响应使S-CO2成为电网频率调节和备用电源应用的首选。
主要应用场景
电网规模的长期储能和负载转移
当与光伏系统等可再生能源结合使用时,S-CO2技术可以提供10至16小时的连续电力。它有效地解决了风能和太阳能的间歇性问题。例如,中国计划在甘肃建设一个50兆瓦的超临界二氧化碳太阳能储能项目,以实现夜间连续发电,预计储能成本比锂电池系统低30%。
工业余热回收与高效发电
钢铁和水泥等行业会产生大量中高温废热(300-600°C),传统方法无法有效利用。S-CO2系统可以直接回收这些废热用于发电,与汽轮机相比,效率超过15%。例如,山东的一家钢铁厂的余热发电效率从22%提高到35%,年发电量增加了2000万千瓦时。

下一代核能与清洁供暖
S-CO2系统与高温气冷反应堆的集成可以产生超过50%的效率(传统核电站的运行效率约为33%)。这种配置降低了设备的复杂性和成本,同时将废热重新用于区域供暖,实现了热电联产。
碳捕获和利用储存
利用从燃煤发电厂捕获的二氧化碳作为工作流体,创建了一个闭环系统。这有助于发电,同时最大限度地减少碳排放,有效地推动传统能源向更清洁的替代品过渡。
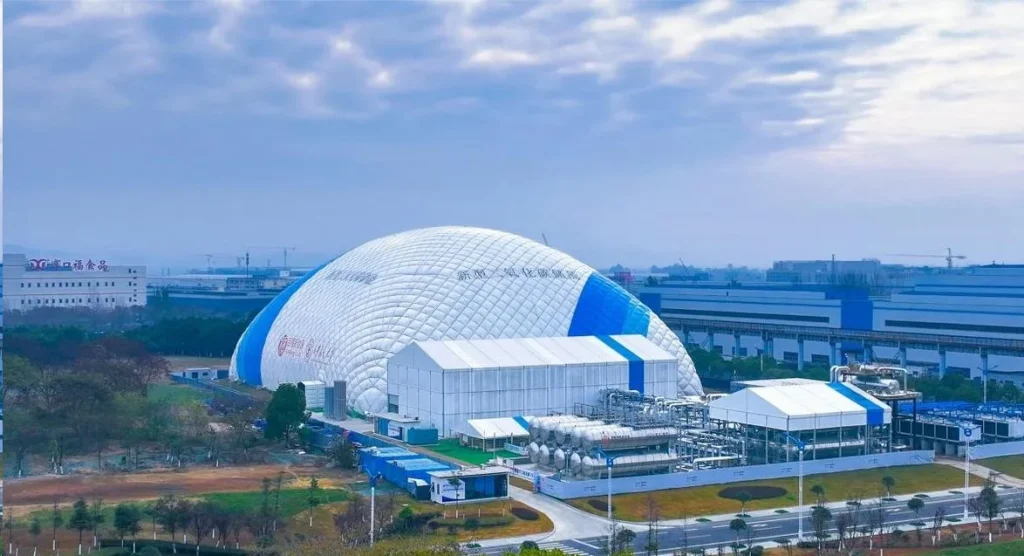

当前的发展和挑战
全球研发进展
在中国,西安热工研究院和清华大学等领先机构已经建立了多个示范项目。例如,西安1兆瓦超临界二氧化碳储存示范机组将连续运行72小时,效率为48%。
在国际上,桑迪亚国家实验室和德国DLR等组织正在进行20兆瓦的试点测试,预计到2030年将实现商业化。西班牙阿本戈阿正在摩洛哥规划首个50兆瓦的“太阳能热+s-CO2储能”项目。
关键挑战
- 材料耐温性:在超过700°C的环境中,二氧化碳的腐蚀性会对钢材料构成重大挑战,因此需要开发新的镍基合金或涂层,这可能会很昂贵。
- 系统集成复杂性:压缩机和涡轮机等高压部件需要精确的制造公差(微米级),以确保长期稳定运行。
- 初期投资高:目前100兆瓦项目的成本约为1500万元/兆瓦时,是锂电池系统的2到3倍,需要规模经济来降低成本(预计到2035年将降低40%)。
二氧化碳充电技术利用了超临界二氧化碳的高效能量转换能力,克服了传统的热循环效率障碍,同时提供了高功率密度、环保和多能源耦合的优势。随着这项技术在示范阶段之后的发展,它在长期储能、工业能效和碳中和等对全球能源转型至关重要的关键领域具有巨大潜力。
关于长江装备
长江装备空气圆顶团队专门为各种应用提供多样化且具有成本效益的充气圆顶解决方案,如军事、工业、文化和体育、娱乐和农业用途的空气圆顶,受到广泛行业的信赖。
如果您正在为您的项目探索可持续且经济高效的充气圆顶解决方案,请随时在此处获取免费的专业建议。让我们携手迈向更绿色的未来!